Walnut trees are a valuable crop but are susceptible to various diseases that can reduce yields and compromise the quality of the nuts. In this article, we will discuss some of the main walnut diseases, how to recognize them, and how to manage them effectively.
Tilletiа
What is it?
Tilletia is a fungal disease that affects various plants, including walnuts. It belongs to the group of "smut" pathogens that form spores and infect plant seeds and tissues. In walnuts, it can cause significant yield losses and degrade nut quality.
How to recognize it?
-
- Black, shriveled nuts
- Unpleasant odor reminiscent of rot
- Gray-black spore coating that can spread to other fruits
- Infection may start during flowering and develop throughout fruit growth


How to control it?
- Conventional farming: Spraying with fungicides based on copper, tebuconazole, or propiconazole, especially in the early stages of development.
- Organic farming: Use of copper-based products (in limited doses) and biofungicides such as Trichoderma harzianum.
Alternariosis
What is it?
Alternariosis is a fungal disease caused by the Alternaria species, attacking leaves, fruits, and young shoots of walnut trees. It thrives in high humidity and warm temperatures.
How to recognize it?
- Dark brown-black spots on leaves and green walnuts
- Spots often have a yellowish halo around them
- Leaves begin to yellow, dry out, and fall off
- Walnuts rot and fall prematurely
- Advanced stages lead to significant yield losses


How to control it?
- Conventional farming: Spraying with fungicides such as mancozeb, chlorothalonil, azoxystrobin, or captan.
- Organic farming: Use of biodegradable fungicides such as Bacillus subtilis and copper-based products.
Yellow Sporulation
What is it?
Yellow sporulation is a fungal disease caused by specific pathogens that lead to discoloration and reduced photosynthetic activity in leaves.
How to recognize it?
- Irregular yellow spots on leaves
- Premature leaf drop
- Reduced walnut tree growth
- Discoloration of fruits, potentially leading to lower nut quality


How to control it?
- Conventional farming: Spraying with copper-based or systemic fungicides.
- Organic farming: Application of biofungicides such as Bacillus subtilis and the use of sulfur-based organic products.
Insect Damage
What is it?
Insects can cause severe damage to walnuts by attacking both leaves and fruits. Common pests include the codling moth (Cydia pomonella), walnut weevil (Curculio nucum), and various leaf-chewing caterpillars.
How to recognize it?
- Holes in nuts and fruits
- Larvae inside the nuts
- Premature fruit drop
- Drying of young shoots

How to control them?
- Conventional farming: Use of insecticides such as deltamethrin, lambda-cyhalothrin, or thiamethoxam.
- Organic farming: Biological control through attracting natural enemies like parasitic wasps, using pheromone traps, and spraying with natural insecticides such as neem oil.
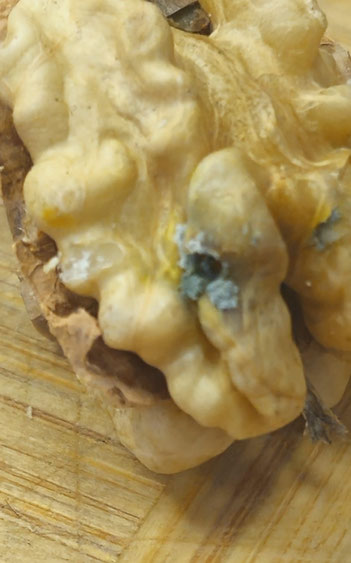
Green Mold - Penicillium
What is it?
A fungal disease caused by the Penicillium species, affecting stored nuts and leading to the formation of green mold colonies.
Possible causes of green mold:
- Mold growth during storage due to high humidity and poor ventilation
- Fungal infections such as Penicillium spp. that cause nut decay
- Mycotoxins (aflatoxins) that reduce nut quality and can be hazardous to health
How to recognize it?
-
- Green coating on the nut surface
- Rotting and unpleasant odor
- Reduced quality and edibility of the nuts
- Possible production of mycotoxins, which are harmful to human health

How to control it?
- Conventional farming: Spraying with fungicides such as iprodione or thiabendazole during storage.
- Organic farming: Use of biological preservatives such as Pseudomonas fluorescens and proper storage of walnuts in dry and well-ventilated areas.
Combating walnut diseases requires a comprehensive approach, including regular monitoring, preventive measures, and timely treatments. Maintaining good agricultural practices, using appropriate treatments (both conventional and organic), and implementing sanitation measures can significantly reduce the risk of diseases and ensure high-quality yields.


Write a comment